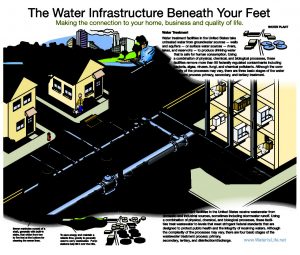
The vast and intricate network of pipes buried beneath our feet is one of the key contributors to the economic success of our nation. Unfortunately, much of our water infrastructure was installed prior to WWII, with some east coast pipes dating back to the late 1800s. Also, many of our nation’s wastewater treatment plants were built in response to the passage of the 1974 Clean Water Act and are now 30-40 years old. Therefore, much of our nation’s water and wastewater infrastructure has reached the end of its useful life and requires repair or replacement.
The ASCE gave both Drinking Water and Wastewater a “D†grade in its 2013 Report Card for America’s Infrastructure; and because water has been so historically undervalued in America, municipalities simply do not have the funds to make the required improvements. In fact, a 2002 US EPA study titled Clean Water and Drinking Gap Analysis Report compared America’s drinking water and wastewater infrastructure needs to the available revenues of utilities. Without including exacerbating factors such as population growth or climate change, the report showed a projected gap in funding over the next 20 years of over $500 billion.
Certainly, our nation must find a way to bridge the funding gap, which will require rate increases and, therefore, community education on conservation practices as well as the value of water. And while these rate increases will provide a portion of the necessary funding, utilities and consumers alone cannot carry the full burden of the funding gap. Thankfully, there are myriad funding opportunities available to assist communities with critical water and wastewater improvements, some of which are listed below:
USDA Rural Development Water & Waste Disposal Loan & Grant Program

The USDA Rural Development (RD) Water & Waste Disposal Loan & Grant Program provides funding for clean and reliable drinking water systems, sanitary sewage disposal, sanitary solid waste disposal, and stormwater drainage to households and businesses in eligible rural areas. This program assists qualified applicants that are not otherwise able to obtain commercial credit on reasonable terms. Areas that may be served include rural areas and towns with fewer than 10,000 people, tribal lands in rural areas, and colonias.
USDA RD funding provides long-term, low-interest loans which may be combined with grants if necessary to keep user costs reasonable. Funds may be used to finance the acquisition, construction, or improvement of drinking water sourcing, treatment, storage and distribution; sewer collection, transmission, treatment, and disposal; solid waste collection, disposal and closure; and stormwater collection, transmission, and disposal.
Clean Water State Revolving Fund (CWSRF) Program

Established by the 1987 amendments to the Clean Water Act, the CWSRF Program is a federal-state partnership that provides a permanent, independent source of low-cost financing to communities for a wide range of water quality infrastructure projects. The program is a powerful partnership between EPA and the states that gives states the flexibility to fund a range of projects that address their highest priority water quality needs.
Using a combination of federal and state funds, state CWSRF programs provide loans to eligible recipients for many types of water infrastructure projects, including construction of publicly owned treatment works; nonpoint source; national estuary program projects; decentralized wastewater treatment systems; stormwater; water conservation, efficiency, and reuse; watershed pilot projects; energy efficiency; water reuse; security measures at publicly owned treatment works; and technical assistance.
Drinking Water State Revolving Fund (DWSRF) Program

The DWSRF Program is a federal-state partnership to help ensure safe drinking water. Created by the 1996 Amendments to the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA), the DWSRF is a financial assistance program to help water systems and states achieve the health protection objectives of the SDWA. The program is a powerful partnership between EPA and the states. Building on a federal investment of over $17.3 billion, the state DWSRFs have provided more than $27.9 billion to water systems through 2014. This assistance was provided through over 11,400 assistance agreements for improving drinking water treatment; fixing leaky or old pipes (water distribution); improving source of water supply; replacing or constructing finished water storage tanks; and other infrastructure projects needed to protect public health.
The DWSRF Program funds a wide range of drinking water infrastructure projects, including treatment projects to install or upgrade facilities to improve drinking water quality to comply with SDWA regulations; transmission and distributionrehabilitation, replacement, or installation to improve water pressure to safe levels or to prevent contamination caused by leaky or broken pipes; rehabilitation of wells or development of eligible sources to replace contaminated sources; installation or upgrade of finished water storage tanks to prevent microbiological contamination from entering the distribution system; interconnecting two or more water systems; constructing a new system to serve homes with contaminated individual wells; and consolidating existing systems into a new regional water system.
Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (WIFIA)

Enacted in 2014 as part of the Water Resources and Reform Development Act, WIFIA establishes a financing mechanism for water and wastewater infrastructure projects to be managed by EPA Headquarters. The WIFIA program provides low interest rate financing for the construction of water and wastewater infrastructure. Funded projects must be nationally or regionally significant, and individual projects must be anticipated to cost no less than $20 million.
WIFIA works separately from, but in coordination with, the State Revolving Fund (SRF) programs to provide subsidized financing for large dollar-value projects. Eligible projects include CWSRF eligible projects; DWSRF eligible projects; projects for enhanced energy efficiency at drinking water and wastewater facilities; acquisition of property if it is integral to the project or will mitigate the environmental impact of a project; bundled SRF projects submitted under one application by an SRF program; and combinations of projects secured by a common security pledge.
Northern Border Regional Commission (NBRC)

The NBRC was formed by Congress in 2008 in order to help fund economic and community development projects in Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York. NBRC was formed to help alleviate distress in the hard-hit northern counties of each state. Bordering Canada, these counties generally have higher levels of unemployment, population loss, and lower incomes.
Eligible projects include those that develop the transportation, telecommunication, and basic public infrastructure within the region; assist the region in obtaining job skills and employment related education, as well as entrepreneurship, technology, and business development; provide basic health care and other public services for those areas that are severely economically distressed and underdeveloped; encourage resource conservation, tourism, recreation, and preservation of open spaces in a manner consistent with economic development goals; or support the development of renewable and alternative energy sources.
Other Funding Sources

In addition to those listed above, there are many other funding sources. Some of these include SWMI Grants, Water Infrastructure Assessment and Planning Grants, Community Block Development Grants (CBDG), and Watersheds & Water Quality in Massachusetts; Water Infrastructure Finance Authority of Arizona (WIFA) and Water and Wastewater Energy Efficiency Rebates through Arizona Public Service (APS) in Arizona; State Aid Grant Program (SAG) in New Hampshire; and Texas Water Development Fund (TWDF), Economically Distressed Areas Program (EDAP), Rural Water Assistance Fund (RWAF), and the State Participation Program (SPP) in Texas.
In Conclusion
Investing in water and wastewater infrastructure now is critical to the sustainability of our economy and the health of our nation. By implementing necessary rate increases and conservation techniques along with community education and robust funding assistance, our nation will have the ability to successfully to bridge the infrastructure funding gap and ensure the economic and environmental viability of our nation for both present and future generations.